Steel Tubing – Expanding Industrial Sector
 What is a Steel tube? A tube is an extended hollow chamber utilized either for transferring fluids i.e. liquids and gases or to guard electrical, optical wires. A tube which is manufactured by any steel grade is known as steel tube.
What is a Steel tube? A tube is an extended hollow chamber utilized either for transferring fluids i.e. liquids and gases or to guard electrical, optical wires. A tube which is manufactured by any steel grade is known as steel tube.
What is Steel Tubing? Steel Tubing is the process of manufacturing a steel tube; normally there are two methods of manufacturing tube namely seamless tubing and welding tubing.
What are Pipes & Why are Pipes confused with tubes? The terms “pipe” and “tube” are confused with each other, however there is a technical difference in both the terminologies. The motive behind a pipe is to carry fluid and the designating criterion is it’s inside volume or the inner diameter. On the other hand tubes are based on the outer diameter. The inner diameter of a tube relies on the thickness of the tube. Tolerances of the tubes are more specific against pipes, this is the reason tubes are costly to manufacture than usual pipes.
Types of Tubes W.R.T Manufacturing Processes: There are mainly two types of tubes on the basis of manufacturing process, these are stated as: Seamless Tubes & Welded Tubes
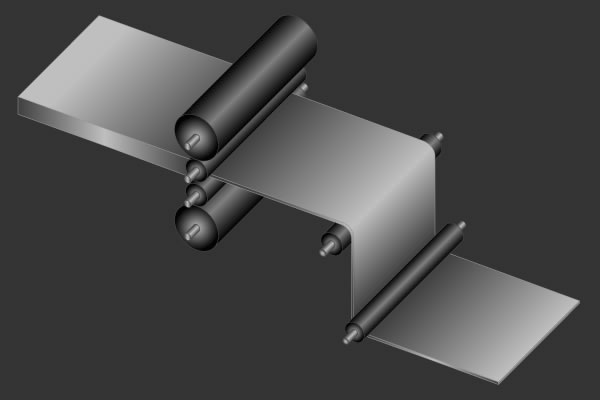
Seamless Tubes: The dissimilarity in the manufacturing technique is understandable from the name. Seamless tube is extruded and drawn from a billet. Due to fewer impurities, seamless tubes are considered more homogenous and more corrosion resistant.
Welded tubes: Welded tubes are manufactured from a strip that is shaped by roll forming and welded to structure a tube. Welded tube is significantly less costly than seamless tube and is freely available in extended lengths. The working pressure of welded tube is twenty percent less than that for an analogous seamless tube. The weld area is reflected to be inhomogeneous thus showing altered malleability and less corrosion resistance along with larger dimensional dissimilarity.
Types of Tubes W.R.T Shapes: There are mainly five types of tubes on the basis of shapes, these are stated as: Rectangular Steel tubing, Square Steel Tubing, Oval Steel Tubing, Round Steel Tubing and Telescopic Steel Tubing.
Rectangular Steel tubing: Rectangular steel tubes are those tubes which are in the form of rectangular periphery and can be manufactured by any of the above manufacturing methods.
Square Steel tubing: Square steel tubes are those tubes which are in the form of Square periphery and can be manufactured by any of the above manufacturing methods.
Oval Steel tubing: Oval steel tubes are those tubes which are in the form of Oval periphery and can be manufactured by any of the above manufacturing methods.
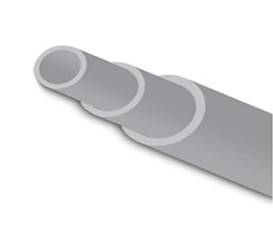
Round Steel tubing: Round steel tubes are those tubes which are in the form of Round periphery and can be manufactured by any of the above manufacturing methods.
Telescopic Steel Tubing: This kind of tube permits another tube or another solid shape to slide inside of it easily. This is usually made by seamless manufacturing method because with weld bead two tubes cannot slide inside over one another with comfort.
Types of Steel Tubes W.R.T Materials: There are mainly three types of steel tubes with respect to the type of material, which are as: Carbon Steel Tubes, Alloy Steel Tubes and Stainless Steel Tubes.
Carbon Steel Tubes: Carbon steel tubes are tubes in which the steel alloying component is carbon in the range of 0.12–2.0%. No other alloy is present in significant alloying percentage. Carbon steel tubes are further classified into mild steel, medium carbon steel tubes, high carbon steel tubes and ultra-high carbon steel tubes. Examples of carbon steel tubes are ST35, E235, (1008/1010), & EN 10305-1.
Alloy Steel Tubes: Alloy steel tubes are tubes that are alloyed with a diversity of elements in between 1.0% to 50% by weight to alter mechanical properties. Alloying material can be chromium, vanadium, molybdenum, silicon and nickel etc. Alloy steels tubes are further classified as low-alloy steels and high-alloy steels. Examples of alloy steels tubes are 4140 Modified, 42CrMo4, SCM440, EN 10083-1 & ASTM A519.
Stainless Steel Tubes: Stainless steel tubes are tubes with a minimum of 10.5% chromium content by mass in its composition. Stainless steel tubes does not spontaneously decompose, rust or stain with environment as normal steel tubes does. Examples of stainless steel tubes are 304, 304L, 316, 316L, ASTM A269, & EN 10088-3.
Calculating the Strength of Steel Tube:
The strength of a steel tube can be calculated by below formula; however a factor of safety is also included so as to give a cushion to design parameters.
Pressure max = (Tensile strength * Wall thickness * 2 / (10 * Outer diameter)) * 10 / Safety factor [Pa]
The pressure that comes out from the above formula also involve factor of safety in it, factor of safety is to be defined by the designer of the steel tube on its own.
Calculating the Weight of a Steel Tube: The mass of a steel tube can be calculated by below formula:
Mass = Density for the type of steel * Material Volume of the Tube
Note: Material Volume of the tube is only the material volume and does not represent the hollow volume of the tube.
Applications of Different Steel Tubes: Steel tubes are used in various applications and thus such tubes are named after its applications such as Water Tubes, Steel Casing Tubes, Sewage Tubes, Structural Steel Tubes, Industrial Steel Tubes, Steel Scaffolding Tubes and Oil & Gas Tubes etc.
Steel tubes are also used in heat exchangers, pressure equipment, mechanical and moving machinery parts, boilers, and at high temperature applications. Tubes are manufactured according to its application, based on the application type of material and manufacturing process is selected.
Inspection of Steel Tubes: There are number of inspection tests performed on steel tubes, only few are areas of inspection & checks are discussed here:
Chemical Composition: The cast product which has to be manufactured into tube is tested for its desired chemical composition, if it lies within the desired range then the product is said to be qualifying the chemical requirements.
Dimensional Inspection: The dimensional values of a tube is inspected, normally its outer diameter, wall thickness and length is inspected against the tolerance values of the desired tube.
Mechanical Properties: Mechanical properties of the steel tube i.e. tensile test, hardness test and impact test are usually carried out against the desired values of tensile strength, hardness, and toughness.
Technological Tests: Technological tests are manipulative testing, it examines whether the tube is manipulative or not and whether it will crack under manipulation of not. These tests include flattening, drift expanding, flanging, bending and ring tensile tests.
Leak Tightness Test: These tests are used to identify whether there are leaks in the tubes or not. These tests include hydrostatic test & non-destructive testing.
Non-Destructive Testing: Non-destructive testing is carried on to check the tubes for any longitudinal, transverse and laminar defects. These tests include eddy current tests, leakage fluxes tests etc.
Other Tests: There are some other tests which are carried out based on demand; these tests examine metallography, & corrosion resistance of steel tubes.
Conclusion: Steel tubes have played a pivotal role in structural engineering. These tubes have evolved new horizons in structural engineering. The combinations of these tubes are used in framed tube, trussed tube, and bundled tube structural units. Some of the success of combinations of these structural tubes exemplifies Willis Tower, which was built in 1973, from the bundled tube structural design and was the tallest building globally till the end of 20th century. The domain of steel tubes is ever expanding with new realizations and acquaintances which are helping the world expand better.





great post